How To Select Your Encoder When Streaming Your Games
Maximize your game streaming quality with our comprehensive guide on encoders. Learn about different types, such as libx264 and NVENC, their pros and cons, and tips for choosing the right one for Twitch and other platforms. Perfect for gamers looking to enhance their streaming setup.

When streaming your games, you will have to broadcast your gameplay to various platforms such as Kick, Glitch, Twitch, and others. However, one of the fundamental aspects of streaming is the use of an encoder.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of encoders, their benefits and drawbacks, and demonstrate their effects by streaming to Twitch and using Glitch as the streaming tool to switch between encoders.
What is an Encoder?
When you set up your streaming and capture your game, the file size is actually huge. It can be gigabytes of data in under a minute, which is far too much for an average user’s internet to download quickly. Thus, the game’s stream must be compressed, and that is what an encoder does.
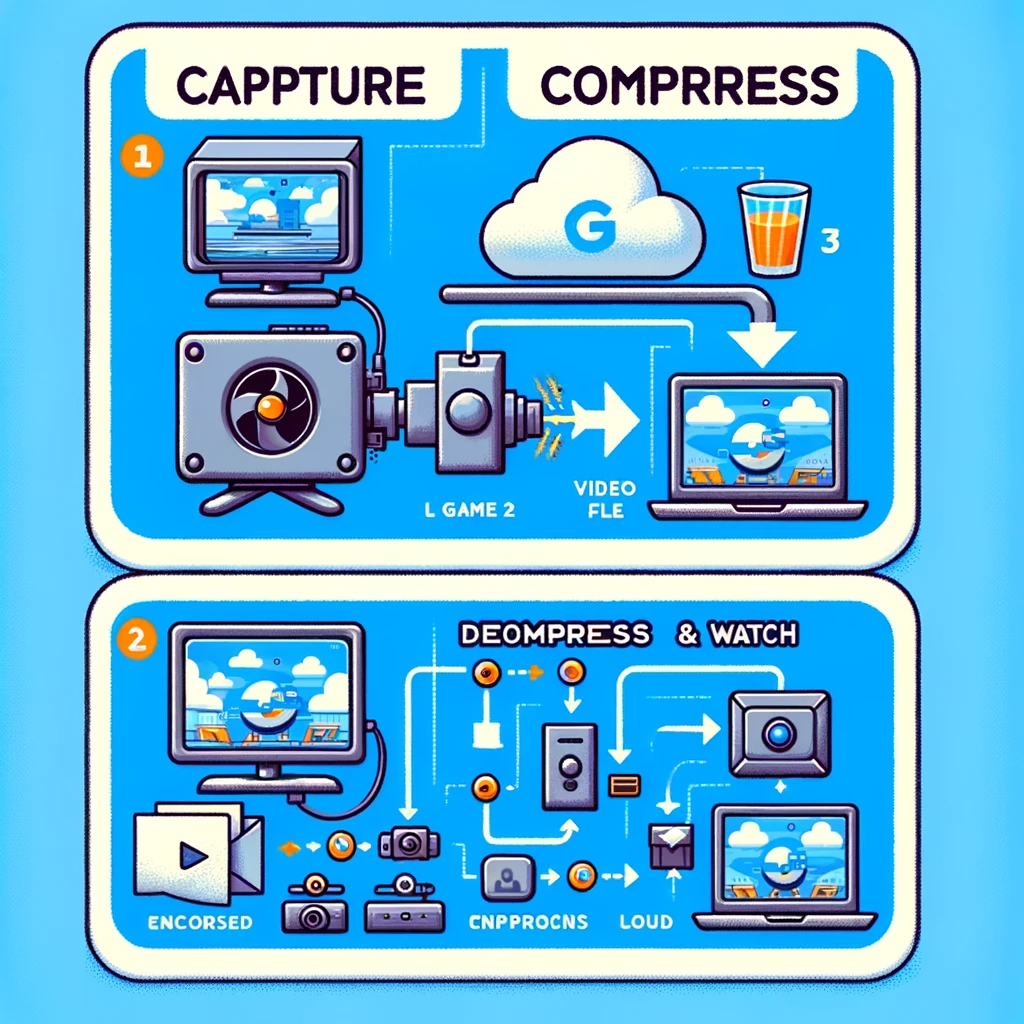
An encoder takes that large video stream and compresses it to a much smaller size. This compressed video file is then sent over the internet as data. When it reaches the user’s computer, the video file is decompressed and returned to its original size and quality, allowing viewers to watch the video.
Advanced Topic - Codecs
For those readers interested in a more advanced topic, such as how compression occurs, we have codecs. This article here goes deeper into what codecs are. Encoders and codecs work together for compression and decompression. The encoder determines whether to run on the CPU or GPU, and the codec controls how the compression and decompression are executed.
Think of the encoder as a car and the codec as its engine. You can swap out different engines, which affects how the car operates; similarly, different codecs can be interchanged. A Ferrari, for instance, will have excellent transmission, superior steering, and the capacity to go really fast with better engines. An older Honda Accord, while you can replace the engine, may not be built to fully utilize all of the engine's power.
The Different Types of Encoders:
There are several types of encoders that can be used for processing you video for live streaming games. A list of them is below.
1. libx264
What it is: libx264 is a software encoder that's super popular for streaming. It's known for producing great video quality without needing a super beefy computer.
Pros:
- It's free and open-source.
- Works on most computers without needing special hardware.
- Offers lots of customization to get your stream looking just right.
Cons:
- It can be heavy on your CPU, especially if you're playing a demanding game.
- Might not be the best choice for less powerful computers.
- Its GPL license may not be suitable for all situations.
2. libopenh264
What it is: This is another software encoder, made by Cisco, that's also free to use. It's a bit simpler than libx264 and focuses on compatibility.
Pros:
- Easy to use and set up.
- Good for running on systems without dedicated graphics cards.
- License cost is covered by Cisco in certain instances.
Cons:
- Can be potentially demanding on your CPU.
- Not as customizable as libx264.
3. NVENC
What it is: NVENC is a hardware encoder that comes with Nvidia's graphics cards. It's like having a mini assistant built into your GPU that's dedicated to encoding your stream.
Pros:
- Takes the load off your CPU, letting your game use more of your computer's brainpower.
- Great for high-quality streams without bogging down your system.
- Fast and efficient, which is perfect for fast-paced games.
Cons:
- Only available if you have an Nvidia graphics card.
- May not always be as high quality all other encoders
4. VAAPI
What it is: VAAPI is a hardware encoder like NVENC but for Linux users. It lets your GPU handle the encoding process, keeping your CPU free to run your game smoothly.
Pros:
- Less stress on your CPU.
- Supports various hardware, giving you flexibility.
Cons:
- Can be tricky to set up.
- Not all games and systems play nice with it.
5. VideoToolbox
What it is: VideoToolbox is hardware encoder for the Mac gamers out there. It's Apple's way of letting your Mac's hardware do the heavy lifting for your stream.
Pros:
- Optimized for Macs, so it runs smoothly.
- Frees up your CPU for your gaming needs.
Cons:
- Only for Mac users.
- Can sometimes be a bottleneck when streaming.
6. QuickSync
What it is: QuickSync is Intel's answer to hardware encoding. If you have an Intel CPU, QuickSync can handle the encoding without adding more stress to your processor.
Pros:
- It's built into many Intel CPUs, so there's a good chance you can use it.
- Lowers the impact on your CPU's performance while gaming.
Cons:
- Video quality can take a hit compared to software encoders like libx264.
- Only available to those with certain Intel CPUs.
- Might not work with CPU intensive games.
Which Encoder Should You Use?
In the descriptions of the above-mentioned encoders, you will see them categorized as either hardware or software. "Hardware" indicates that the encoder uses the GPU for encoding, which is generally more efficient for video because GPUs are optimized for handling graphics. On the other hand, software encoders utilize the CPU, which is more versatile and capable of handling a variety of operations.
When deciding on resource allocation for the game, it's important to understand the demands placed on specific hardware components. If the game is heavily reliant on GPU resources, leaving the CPU with spare capacity, it would be wise to use a software encoder that utilizes the CPU. Conversely, if the game is not very GPU-intensive, and there's available GPU capacity, then a hardware encoder, which uses the GPU for producing the video stream, would be preferable.
1. Assess Your Hardware: First, look at your computer’s CPU and GPU. If you have a strong, multi-core CPU, you might be able to handle a software encoder like libx264 without much trouble. On the other hand, if your CPU is less powerful, or you want to ensure it focuses on running your game, consider using a hardware encoder.
2. Look at the Performance Impact: Run some tests with your game running and the stream going. Monitor your CPU and GPU usage, and watch for dropped frames in the stream or lag in the game. Choose the encoder that gives you the best balance of stream quality and game performance.
3. Quality vs. Speed: You'll need to decide on your balance between quality and encoding speed. Software encoders like x264 can often produce a higher quality stream at the cost of more CPU usage. Hardware encoders might produce a slightly lower quality image but will do so with a much smaller performance impact on your system.
4. Stream Platform Requirements: Check the requirements of your streaming platform (Twitch, YouTube Live, etc.). They usually provide recommended settings for encoders, bitrates, and resolutions.
Examples Of Different Encoder Usage
To demonstrate the quality of different encoders, we are taking the game Rocket League and using a Nvidia’s Hardware Encoder, and two software encoders of OpenH264 and Libx264. We are using Glitch because the streaming tool easily allows use to switch between encoders:
The following where the specs of the computer and stream:
- Streaming Destination: Twitch
- Tool: Glitch Streaming App
- Game: Rocket League
- GPU: Nvidia GeForce RTX 3080
- Chunk Size: 20
- FPS: 60
- GOP: 120
- Resolution: 1920 x 1080
- Bitrate: 7500
Can you tell any difference between any of the videos?
OpenH264
Libx264
Nvidia Nvenc
Wrapping It Up
Choosing the right encoder for streaming your games comes down to balancing quality, performance, and what hardware you have. If you've got a powerful Nvidia card, NVENC might be your best bet. On a less powerful computer? libx264 could be the way to go, as long as you're okay with tweaking settings. And if you're on a Mac, VideoToolbox is your friend.
Remember, the goal is to share your gaming skills with the world without turning your computer into a slideshow. Test out different encoders and settings to find what works best for you and your setup. Happy streaming!




